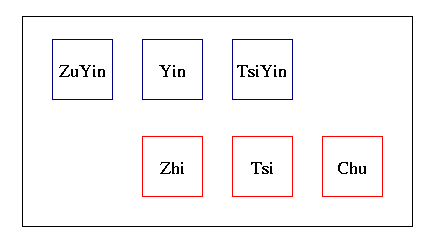
Figure 1. Key Elements of Chinese Language
We identify 6 elements in Chinese language, these elements are key parts in applications. These elements are (as shown in Figure 1)
 Figure 1. Key Elements of Chinese Language |
ZuYin | BoPoMoFo symbols |
| Yin | a meaningful pronunciation | |
| Zhi | a Chinese character | |
| Tsi | a Chinese word | |
| TsiYin | compound of Yin for a Tsi | |
| Chu | a sentence |
Table 1 is a list of potential softwares that may require each of the elements:
| ZuYin | computer aided education, input method engine |
| Yin | input method engine, speaking, voice recognition |
| Zhi | input method engine, word processing |
| Tsi | input method engine, word processing, checker |
| TsiYin | speaking, voice recognition |
| Chu | word processor |
With libtabe, an application enables the knowledge of processing each element, and conversion between them. For example, an application can query a single character or a word frequency by calling a function provided by libtabe, query a single character or a word's pronunciation and reverse lookup. The complexity of processing each element increase from left to right, from top to bottom in Figure 1.
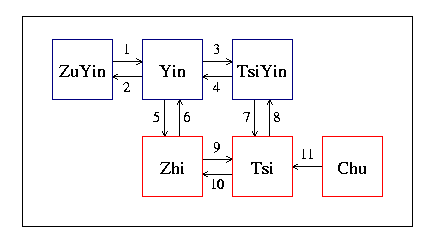
Figure 2 depicts the basic architecture of libtabe. The solid line with one-way arrow means there's a strong relationship and can be converted. All the conversions are supported by libtabe. Detailed explanations on how the conversion are done can be found in Conversion Functions section.
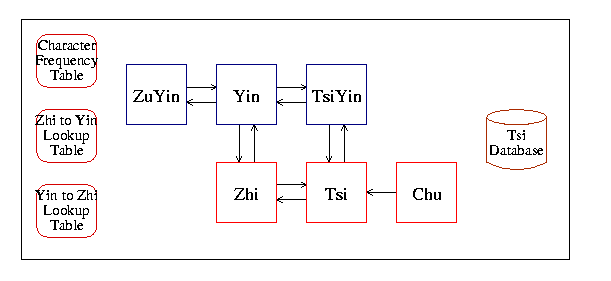
Despite of those elements and conversion functions, there're 3 tables and 1 database have been implemented in libtabe. Two out of the three tables are used by conversion functions, the other one is used to provide character frequency. The Tsi database provides more than 140,000 word, including the pronunciation, frequency. We planned to add some more tables and databases if they are appropriate and useful. They are shown in Figure 3.
There're eleven conversion functions in the basic architecture. Each of them is responsible for converting from one element to another. Applications frequently do conversion between elements to make use of the underlying semantics of language.
| Number | From | To | Description |
| 1 | ZuYin | Yin | encoding |
| 2 | Yin | ZuYin | decoding |
| 3 | Yin | TsiYin | concatenation |
| 4 | TsiYin | Yin | decoupling |
| 5 | Yin | Zhi | table lookup (1-to-many) |
| 6 | Zhi | Yin | table lookup (1-to-many) |
| 7 | TsiYin | Tsi | database query (1-to-many) |
| 8 | Tsi | TsiYin | database query (1-to-many) |
| 9 | Zhi | Tsi | concatenation |
| 10 | Tsi | Zhi | decoupling |
| 11 | Chu | Tsi | word segmentation |
Functions 3, 4, 9, 10 are trivial ones, because of the underlying elements are all fixed length. "BoPoMoFo system and encoding in libtabe" provides useful information about conversion functions 1 and 2.